Being discharged from the hospital with a peripheral intravenous (IV) cannula can be a concerning and confusing experience. However, understanding what a cannula is, why it is used, and how to care for it can help alleviate some of the anxiety. This article aims to provide comprehensive information on what to expect when you are discharged with a peripheral IV cannula, ensuring you are well informed and confident in managing your care at home.

Understanding the Peripheral IV Cannula
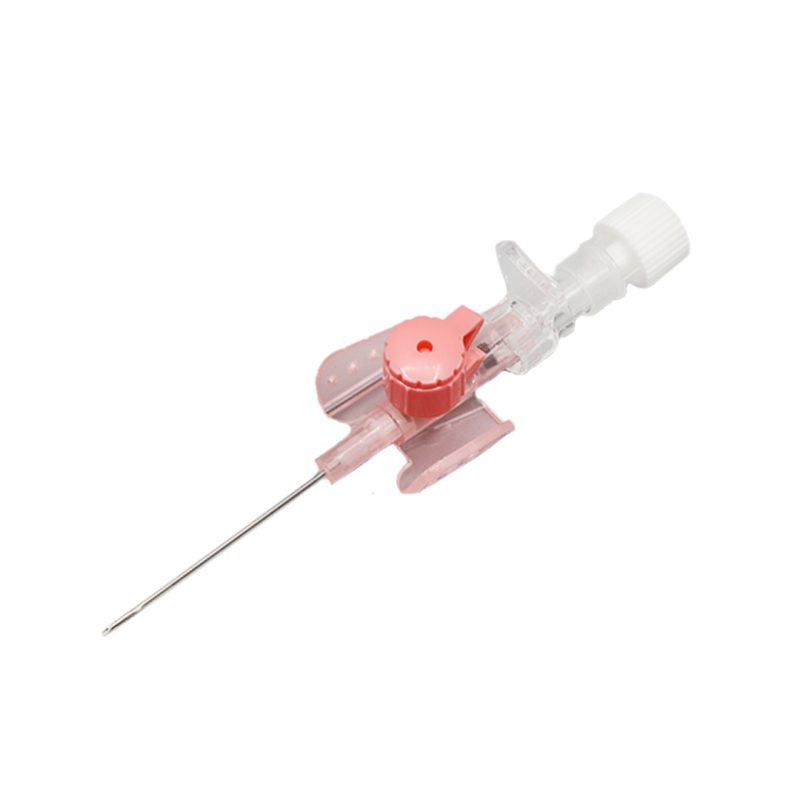
A peripheral IV cannula is a small, flexible tube inserted into a vein, usually in the hand or arm, to administer medications and fluids or draw blood. It’s a standard medical tool used in hospitals and outpatient settings. The cannula consists of a needle, which is used to insert the flexible tube into the vein. Once the tube is in place, the needle is removed, leaving the cannula to deliver treatment directly into the bloodstream.
Why is a Cannula Used?
Cannulas are used for a variety of medical reasons. They allow for the rapid administration of fluids, medications, and nutrients, which is crucial in emergencies or for patients who cannot take medications orally. Cannulas are also used for blood transfusions and drawing blood samples. The ability to administer treatments directly into the bloodstream ensures they work quickly and effectively.
Preparation Before Discharge
Before being discharged with a cannula, medical staff will ensure you are adequately prepared and informed about managing it at home. This includes:
Education and Training
Healthcare providers will provide detailed instructions on how to care for the cannula site. This training may include demonstrations on how to clean the area, recognize signs of infection, and handle minor complications. You may also be given written instructions or a manual to refer to at home.
Supplies
You will be provided with the necessary supplies to care for your cannula. These supplies may include antiseptic wipes, gauze, adhesive dressings, and tape. Ensure you have enough supplies to last until your next medical appointment.
Contact Information
It is essential to have contact information for your healthcare provider or a designated medical professional who can answer any questions or concerns that may arise once you are at home. This could include a phone number or an email address.

At-Home Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance of the cannula are critical to prevent complications such as infections, blockages, or dislodgement. Here are some essential aspects of at-home care:
Cleaning and Dressing the Site
Keeping the insertion site clean is paramount. Follow these steps to ensure proper hygiene:
- Wash Your Hands: Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before touching the cannula or the insertion site.
- Clean the Site: Use antiseptic wipes to clean the area around the cannula at least once a day or as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Change Dressings: Regularly change the dressings that cover the insertion site. Typically, this should be done every 48-72 hours or immediately if the dressing becomes wet, dirty, or loose.
Monitoring for Complications
It’s crucial to monitor the cannula site for any signs of complications. These include:
- Infection: Redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge at the site may indicate an infection. Fever and chills are also signs of a systemic disease.
- Blockage: Difficulty in flushing the cannula or administering medication could indicate a blockage.
- Dislodgement: If the cannula moves or is accidentally pulled out, you may notice pain, bleeding, or the absence of the cannula itself.
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Flushing the Cannula
To prevent blockages, it is essential to flush the cannula regularly with a saline solution. Your healthcare provider will instruct you on how often this needs to be done. The process typically involves attaching a syringe filled with saline solution to the cannula and slowly injecting the solution to ensure the line remains clear.
Activities and Lifestyle Considerations
Living with a cannula involves some adjustments to your daily activities and lifestyle. Here are some considerations:
Physical Activity
While it’s generally safe to engage in light physical activities, it’s important to avoid strenuous exercises or activities that might put pressure on the cannula site. For example, avoid lifting heavy objects or engaging in sports that could result in the cannula being dislodged.
Personal Hygiene
When showering or bathing, take care to keep the cannula site dry. Use a waterproof cover to protect the area. If the site does get wet, dry it immediately and change the dressing.
Diet and Hydration
Maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated can support your overall well-being and recovery. Hydration, in particular, helps maintain good vein health and can make the process of flushing the cannula easier.
Travel Considerations
If you plan to travel, inform your healthcare provider. They can give you additional tips and provide extra supplies for the journey. It’s also advisable to have a letter from your healthcare provider explaining the cannula and its necessity, which can be helpful when going through security checks at airports.
When to Seek Medical Help
Understanding when to seek medical help is critical. Immediate medical attention should be sought if you experience:
- Persistent pain or swelling at the cannula site.
- Signs of infection, such as increasing redness, warmth, pus, or a foul odor.
- Fever or chills.
- The cannula has come out or appears dislodged.
- Difficulty in flushing the cannula or administering medications.
Routine Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor the cannula and your overall health. During these appointments, the cannula site will be checked, and any necessary adjustments to your care plan will be made. These visits are also an excellent opportunity to address any concerns or questions you may have.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations
Adjusting to life with a cannula can be emotionally and psychologically challenging. It’s not uncommon to feel anxious or frustrated. Here are some tips to manage these feelings.
Stay Informed
Knowledge is empowering. The more you understand the cannula and its purpose, the more confident you will feel in managing it. Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for information and resources.
Support Systems
Lean on your support system, which may include family, friends, or a support group for patients with similar medical conditions. Talking about your experiences and concerns can provide emotional relief.
Professional Help
If feelings of anxiety or depression become overwhelming, consider seeking help from a mental health professional. They can provide strategies to cope with the emotional aspects of your condition.
Conclusion
Being discharged with a peripheral IV cannula requires careful management and vigilance to ensure your health and well-being. Understanding what a cannula is, why it is used, and how to care for it at home can significantly reduce the risk of complications and make your recovery smoother. Always follow the instructions provided by your healthcare team, keep the insertion site clean, monitor for signs of infection or other issues, and maintain regular communication with your healthcare provider. With proper care and attention, you can manage your cannula effectively and focus on your recovery and well-being.












Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.