Foot pain is a prevalent issue that affects people of all ages, from athletes to those with sedentary lifestyles. Understanding the various types of foot pain and their causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. This article provides a comprehensive guide to identifying common foot problems using a foot pain chart, explaining the symptoms, causes, and possible treatments for each condition.
Common Causes of Foot Pain
Foot pain can originate from various sources, including injury, overuse, and medical conditions. Identifying the root cause is the first step in finding relief. Below are some of the most common causes of foot pain.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It occurs when the thick band of tissue running across the bottom of the foot (the plantar fascia) becomes inflamed. This condition is often caused by repetitive strain or overuse, particularly in runners and people who spend long hours on their feet. Symptoms include sharp pain in the heel, especially noticeable with the first steps in the morning or after long periods of rest. Treatment options include rest, ice, stretching exercises, and, in severe cases, physical therapy or corticosteroid injections.

Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This condition commonly affects runners who suddenly increase the intensity or duration of their runs. Symptoms include pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, particularly in the morning or after exercise. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications. Stretching and strengthening exercises can also help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Bunions
A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe. This deformity can cause significant pain and swelling, making it difficult to wear shoes. Bunions are often hereditary but can be exacerbated by wearing tight, narrow shoes. Symptoms include a swollen, red, and painful bump on the outside of the big toe joint. Treatment options range from wearing wider shoes and using orthotic devices to surgical intervention in severe cases.
Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes, usually between the third and fourth toes. This condition can cause sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot and a sensation of having a pebble in the shoe. High-heeled shoes and activities that put pressure on the ball of the foot can contribute to the development of Morton’s neuroma. Treatment includes changing footwear, using orthotics, and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery.
Flat Feet
Flat feet, or fallen arches, occur when the arches of the feet are low or nonexistent. This condition can lead to foot pain and problems with walking or running. Flat feet can be hereditary or result from injury, aging, or obesity. Symptoms include pain and swelling along the inner side of the feet and problems with balance. Treatment may involve supportive shoes, orthotic inserts, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, surgery.
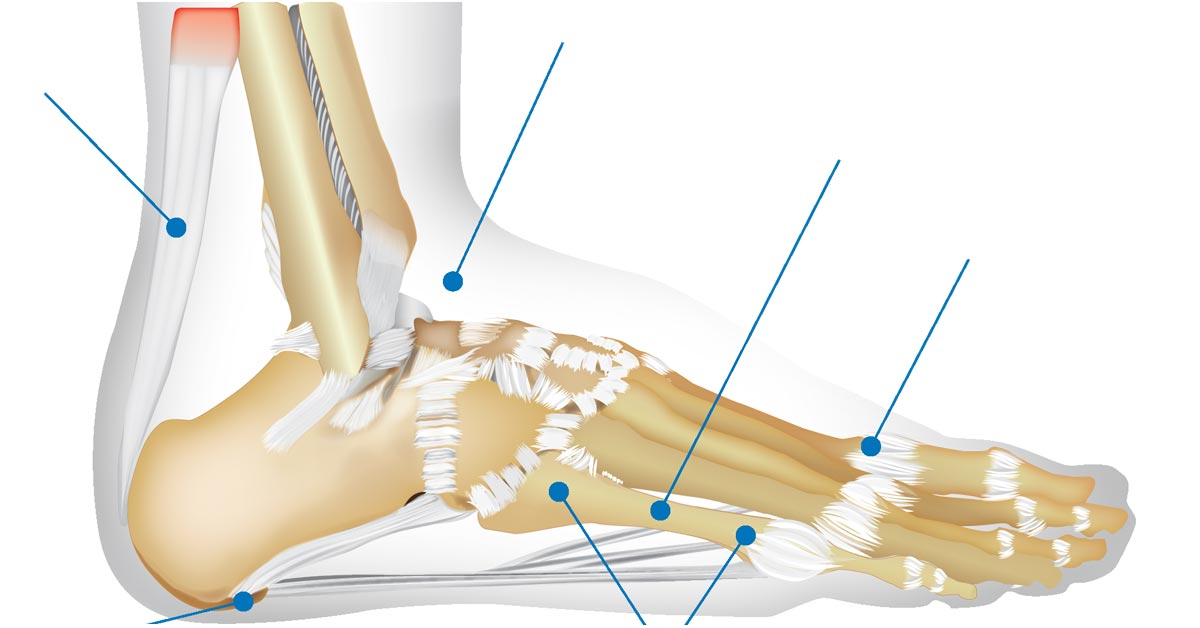
Foot Pain Chart: Locating and Diagnosing Pain
A foot pain chart is a useful tool for pinpointing the exact location of foot pain and correlating it with potential causes. By identifying the specific area of discomfort, individuals can better understand the underlying issue and seek appropriate treatment.
Heel Pain
Heel pain is commonly associated with conditions such as plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinitis. Pain concentrated on the bottom of the heel typically points to plantar fasciitis, while pain at the back of the heel is more indicative of Achilles tendinitis. Both conditions often result from overuse or improper footwear and can be managed with rest, ice, stretching, and supportive shoes.
Arch Pain
Plantar fasciitis, flat feet, or muscle strain can cause pain in the arch of the foot can cause pain in the arch of the foot. Plantar fasciitis pain is often felt in the arch, especially after periods of inactivity. Flat feet can lead to muscle fatigue and strain, causing pain in the arches. Proper arch support, stretching exercises, and orthotics can help alleviate this type of pain.
Ball of Foot Pain
Pain in the ball of the foot, or metatarsalgia, can be due to Morton’s neuroma, stress fractures, or overuse injuries. Morton’s neuroma typically causes a sharp, burning pain between the toes, while metatarsalgia results in a more generalized pain in the ball of the foot. Wearing shoes with adequate cushioning and avoiding high heels can help reduce this pain. In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary.
Toe Pain
Toe pain can arise from various conditions, including bunions, hammertoes, and gout. Bunions cause pain on the side of the big toe, while hammertoes result in pain and deformity of the smaller toes. Gout, a type of arthritis, often affects the big toe with sudden, severe pain. Treatment depends on the specific condition but may include wearing proper footwear, taking anti-inflammatory medications, or, in the case of gout, dietary changes.
Ankle Pain
Ankle pain is often related to sprains, arthritis, or tendinitis. Ankle sprains occur when the ligaments supporting the joint are stretched or torn, usually due to an awkward twist or roll. Arthritis can cause chronic pain and stiffness in the ankle joint, while tendinitis results from overuse or injury to the tendons around the ankle. Treatment for ankle pain typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
Preventing Foot Pain
Preventing foot pain involves a combination of proper footwear, regular exercise, and good foot hygiene. By taking proactive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing common foot problems.
Choosing the Right Footwear
Wearing the right shoes is crucial for preventing foot pain. Shoes should provide adequate support, cushioning, and room for the toes. High heels and tight shoes can lead to conditions like bunions and Morton’s neuroma. It’s important to select shoes that match the activity, whether it’s running, walking, or standing for long periods.
Regular Exercise and Stretching
Regular exercise and stretching can strengthen the muscles and ligaments in the feet, improving overall foot health. Stretching exercises, such as calf stretches and toe stretches, can help prevent conditions like plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinitis. Strengthening exercises, including toe curls and heel raises, can enhance the stability and support of the feet.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put additional stress on the feet, leading to pain and conditions such as plantar fasciitis and arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce the strain on the feet and improve overall foot health.
Practicing Good Foot Hygiene
Good foot hygiene is essential for preventing infections and other foot problems. This includes keeping the feet clean and dry, trimming toenails regularly, and checking for any signs of injury or infection. Moisturizing the feet can also prevent dry, cracked skin, which can lead to further complications.
When to Seek Medical Help
While many cases of foot pain can be managed with home remedies and preventive measures, some situations require medical attention. If the pain is severe, persistent, accompanied by swelling, redness, or other concerning symptoms, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare professional.

Persistent Pain
If foot pain persists despite home treatment, it may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical evaluation. Conditions such as stress fractures, severe tendinitis, or nerve issues may need specialized treatment.
Swelling and Redness
Swelling and redness can be signs of infection or inflammation. If left untreated, infections can spread and cause serious complications. If you notice these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly.
Difficulty Walking
If foot pain makes it difficult to walk or perform daily activities, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. This could be a sign of a significant injury or condition that requires professional treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing foot pain is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. By using a foot pain chart to identify the specific location and type of pain, individuals can take appropriate steps to manage their symptoms and seek professional help when necessary. Preventive measures, such as wearing proper footwear, regular exercise, and good foot hygiene, can significantly reduce the risk of common foot problems. Taking proactive steps to care for your feet can lead to a more active, pain-free lifestyle.
Also, Read The Following: do i have lice or am i paranoid.











Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.