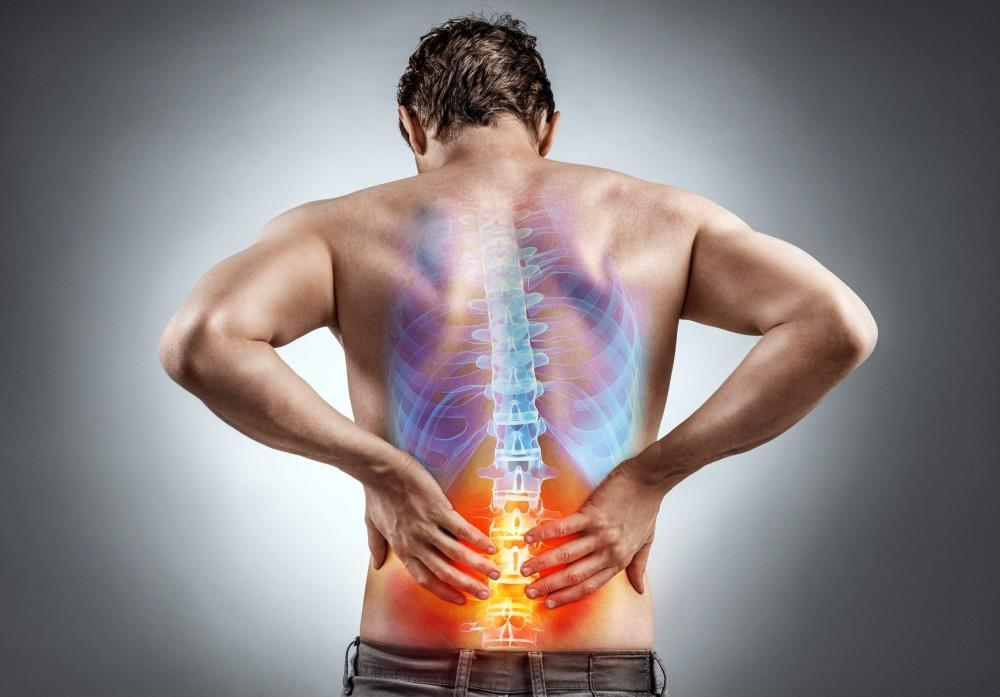
Spinal stenosis is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to significant pain and discomfort. This condition is often age-related, though it can also result from congenital spinal defects, injuries, or degenerative changes in the spine. Patients with spinal stenosis frequently experience pain, numbness, and muscle weakness, particularly in the lower back and legs. Finding effective pain relief is crucial for maintaining quality of life. This article delves into the best painkillers for managing spinal stenosis, providing a comprehensive guide on what works best for relief.
Understanding Spinal Stenosis and Its Symptoms
Before exploring pain relief options, it’s essential to understand spinal stenosis and its symptoms. The spinal canal houses the spinal cord and nerves, and when this canal narrows, it can compress these structures, leading to various symptoms. The most common form, lumbar spinal stenosis, affects the lower back and is characterized by pain, cramping, or numbness in the legs, especially after walking or standing for long periods. Cervical spinal stenosis, affecting the neck, can cause similar symptoms in the arms and shoulders. These symptoms can severely impact daily activities, making effective pain management a priority.
Over-the-Counter Painkillers
Over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers are often the first line of defense for managing spinal stenosis pain. These medications are readily available and do not require a prescription.

Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen, commonly known by the brand name Tylenol, is a widely used OTC painkiller. It works by blocking pain signals in the brain and is often recommended for mild to moderate pain. While acetaminophen is generally well-tolerated, adhering to the recommended dosage is essential to avoid potential liver damage. For many patients with spinal stenosis, acetaminophen can provide sufficient relief for daily pain management.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve), are another popular choice for managing spinal stenosis pain. These medications not only relieve pain but also reduce inflammation, which can be a significant contributor to spinal stenosis symptoms. NSAIDs are beneficial for patients who experience pain due to inflammation around the spinal nerves. However, long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to gastrointestinal issues, such as ulcers and bleeding, and may also impact kidney function. Therefore, it is crucial to use these medications as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Prescription Painkillers
When OTC medications are insufficient for managing spinal stenosis pain, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications. These prescription painkillers are more potent and often provide more significant relief but come with a higher risk of side effects and dependency.
Opioids
Opioids, such as oxycodone (OxyContin), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and morphine, are potent painkillers that can provide substantial relief for severe spinal stenosis pain. They work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking pain signals. However, opioids carry a high risk of addiction and dependency, making them a last resort for many healthcare providers. Additionally, opioids can cause side effects such as drowsiness, constipation, and nausea. Patients prescribed opioids should be closely monitored by their healthcare provider to manage these risks effectively.
Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants, such as cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) and methocarbamol (Robaxin), are often prescribed to relieve muscle spasms and tension associated with spinal stenosis. These medications can help reduce pain and improve mobility by relaxing the muscles around the affected area. Muscle relaxants are typically used with other pain relief methods. Due to potential side effects like drowsiness, dizziness, and dry mouth, they are usually prescribed for short-term use.
Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants
Certain antidepressants and anticonvulsants can also be effective in managing spinal stenosis pain. Medications such as amitriptyline (Elavil) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are commonly prescribed for nerve pain, which is a significant component of spinal stenosis. These drugs work by altering the way the brain perceives pain signals, providing relief for chronic pain conditions. While these medications can be effective, they also have potential side effects, including weight gain, dry mouth, and fatigue. Patients need to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider.
Topical Pain Relievers
Topical pain relievers offer an alternative method for managing spinal stenosis pain. These medications are applied directly to the skin over the painful area and can provide localized relief with fewer systemic side effects.
Capsaicin Cream
Capsaicin, derived from chili peppers, is a common ingredient in topical pain relief creams. It works by depleting substance P, a chemical that transmits pain signals to the brain. Capsaicin cream can be effective in reducing localized pain and is available OTC. Patients should know that it can cause a burning sensation upon application, which typically diminishes with continued use.
Lidocaine Patches
Lidocaine patches are another option for localized pain relief. These patches contain a local anesthetic that numbs the area to which they are applied, providing temporary relief from pain. Lidocaine patches are available by prescription and are generally well-tolerated, though some patients may experience skin irritation at the application site.
Alternative and Complementary Pain Relief Methods
In addition to pharmacological treatments, alternative and complementary methods can significantly manage spinal stenosis pain. These methods often focus on improving overall spine health and reducing pain through non-drug approaches.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of spinal stenosis management. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Physical therapy can also include manual therapy techniques, such as massage and spinal manipulation, to alleviate symptoms.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. This practice stimulates the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms and improves energy flow. Some studies have shown that acupuncture can be effective in reducing chronic pain, including pain from spinal stenosis.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care involves spinal adjustments and manipulations to improve spinal alignment and function. Chiropractors use hands-on techniques to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves, which can reduce pain and improve mobility. While chiropractic care can benefit some patients, seeking care from a licensed and experienced chiropractor is essential to avoid potential complications.

Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness, can also help manage spinal stenosis pain. These practices focus on reducing stress and promoting relaxation, which can alleviate pain and improve overall well-being. Incorporating mind-body techniques into a comprehensive pain management plan can provide additional benefits beyond pain relief.
Personalized Pain Management Plans
Given the variety of pain relief options available, patients with spinal stenosis must work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized pain management plan. This plan should consider the severity of the pain, the underlying causes of spinal stenosis, and the patient’s overall health and preferences. Combining multiple treatment modalities, including medications, physical therapy, and alternative therapies, can often provide the most effective and comprehensive relief.
Conclusion
What is the best painkiller for spinal stenosis involves considering a range of options, from OTC medications to prescription drugs and alternative therapies. Each patient’s experience with spinal stenosis is unique, and what works best for one person may not be as effective for another. By understanding the various pain relief options and working closely with a healthcare provider, patients can develop a tailored approach to managing their pain and improving their quality of life. Whether through medication, physical therapy, or complementary methods, effective pain relief is possible for those living with spinal stenosis.
Also, Read The Following: foot pain chart.










Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.